It's very common to switch devices or change O365 tenants. After a user is activated, multiple locations must be cleared to reset the application to a clean state.
In this article
- Step 1: Remove Office 365 license for subscription-based installations
- Step 2: Remove cached identities in HKCU registry
- Step 3: Remove the stored credentials in Credential Manager
- Step 4: Clear persisted locations
- OLicenseCleanup.vbs
Step 1: Remove Office 365 license for subscription-based installations
Note
If Shared Computer Activation (SCA) is enabled and running, you shouldn't see any product keys installed during the procedure. If you're trying to set up SCA on a computer, make sure to clean up existing keys first.
Note
The ospp.vbs script is in the <Program Files\Microsoft Office\Office16> folder. If the 32-bit version of Office is installed on a 64-bit operating system, the script is in the <Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Office\Office16 folder>. Before running the ospp.vbs command, set the correct directory by using one of these commands, based on your Office version:
- cd C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Office\Office16
- cd C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Office16
Here's how to remove the Office 365 license:
-
In an elevated command window, run the cd command based on your install location:
ConsoleCopycd "C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Office\Office16"
or
ConsoleCopycd "C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Office16"
-
Run the following cscript command:
Visual Basic ScriptCopycscript ospp.vbs /dstatus
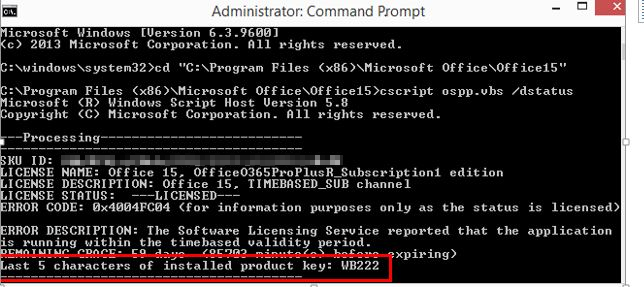
The ospp.vbs command generates a report of the licenses currently in use. The output is in this format:
Note
The report could include multiple licenses. If the output contains a "No installed Product Keys" message after you run ospp.vbs /dstatus, skip the section below and go to "Step 2: Remove cached identities in HKCU registry".
Take note of the Last 5 characters of the installed product key.
-
If a partial product key is returned from /dstatus, run the following command:
Visual Basic ScriptCopycscript ospp.vbs /unpkey:"Last 5 of installed product key"
For example:
Visual Basic ScriptCopycscript ospp.vbs /unpkey:WB222
Repeat the command until all keys are removed.
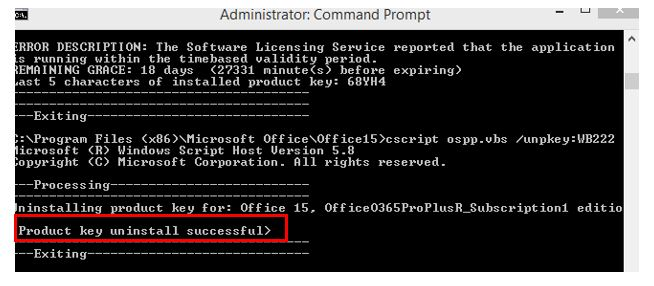
If the output contains the message "product key uninstall successful", close the Command Prompt window and go to Step 2.
Note
For Shared Computer Activation (SCA), remove the tokens listed here: %localappdata%\Microsoft\Office\16.0\Licensing
Step 2: Remove cached identities in HKCU registry
Warning
Follow this section’s steps carefully. Incorrect registry entries can cause serious system issues. As a precaution, back up the registry for restoration.
In Registry Editor, locate the following registry:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Office\16.0\Common\Identity\Identities
Remove all identities under the Identities registry entry.
Note
If you have Shared Computer Licensing enabled, remove the same identities from the registry HKEY_USERS\The user's SID.
Step 3: Remove the stored credentials in Credential Manager
-
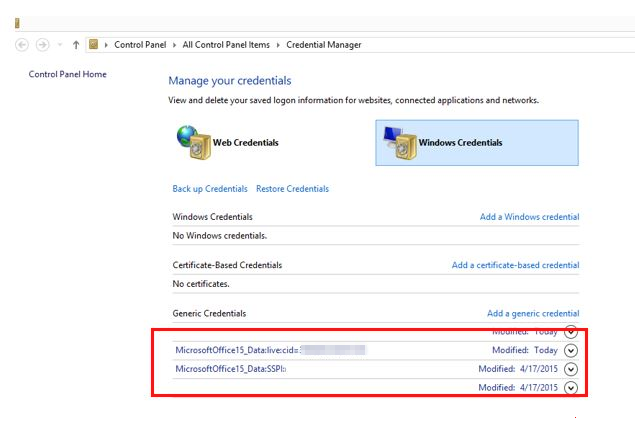
Open Control Panel > Credential Manager.
-
Remove all Windows credentials listed for Office16 by selecting the drop-down arrow and Remove.
Step 4: Clear persisted locations
Clear the following persisted locations if they exist:
Credential Manager
- %appdata%\Microsoft\Credentials
- %localappdata%\Microsoft\Credentials
- %appdata%\Microsoft\Protect
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Protected Storage System Provider
Office 365 activation tokens and identities
- %localappdata%\Microsoft\Office\16.0\Licensing
- %localappdata%\Microsoft\Office\Licenses (Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise version 1909 or later)
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Office\16.0\Common\Identity
- HKEY_USERS\The user's SID\Software\Microsoft\Office\16.0\Common\Identity
OLicenseCleanup.vbs
The four steps above can be automated using OLicenseCleanup.vbs. Simply download and run the script with elevated privileges.
Comments
0 comments
Please sign in to leave a comment.